In modern industries, the selection of pipe materials plays a critical role in ensuring safety and reliability. ASTM A671 steel pipes are specialized pipes produced using electric-fusion welding, designed for low-temperature and high-pressure applications. ASTM A671 is a standard established by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), covering carbon and low-alloy steel pipes fabricated through welding, making it ideal for use in extreme conditions. These pipes are widely utilized in oil and gas transportation, chemical processing plants, boiler systems, and nuclear power facilities. Whether for high-pressure steam transmission or liquid storage in low-temperature environments, ASTM A671 steel pipes deliver exceptional durability and reliability. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the manufacturing process, grade classification, and industrial applications of ASTM A671 steel pipes, offering valuable insights into the features and advantages of this high-performance material!

Overview of ASTM A671 Standard
ASTM A671 is a standard established by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) that specifies requirements for electric-fusion-welded steel pipes. These pipes are primarily designed for low-temperature and high-pressure applications. Manufactured using carbon steel or low-alloy steel plates, ASTM A671 steel pipes undergo strict quality testing, including non-destructive examinations and heat treatment of weld seams, ensuring reliable performance in extreme conditions.
Key Features of ASTM A671
Applications
Ideal for low-temperature environments (e.g., storage and transport of cryogenic liquids) and high-pressure systems (e.g., boilers and high-pressure pipelines).
Material Composition
Available in various ASTM A671 Grades, such as CC60, CC65, and CC70, each suitable for specific pressure and temperature requirements.
Manufacturing Process
Pipes are produced through electric-fusion welding, with optional heat treatment for weld seams to enhance mechanical properties.
Testing and Inspection
Both weld seams and base materials undergo rigorous testing, including tensile tests, impact tests, and non-destructive examinations, ensuring compliance with specific ASTM A671 Classes.
Comparison of ASTM A671 with Other Pipe Standards
ASTM A671: Low-temperature and high-pressure applications, such as tanks and boiler systems. Electric-fusion welded. Flexible Grades and Classes for varied pressure and temperature requirements
ASTM A53: General fluid transport, such as water and gas. Seamless or welded. Includes A53 Carbon Steel, suitable for general pipeline applications
ASTM A106: High-temperature and high-pressure systems, such as refineries and chemical plants. Seamless. Excellent performance in extreme conditions
ASTM A672: High-pressure pipelines, similar to A671 but for high-temperature environments. Electric-fusion welded.Similar to A671 but designed for elevated temperature applications.
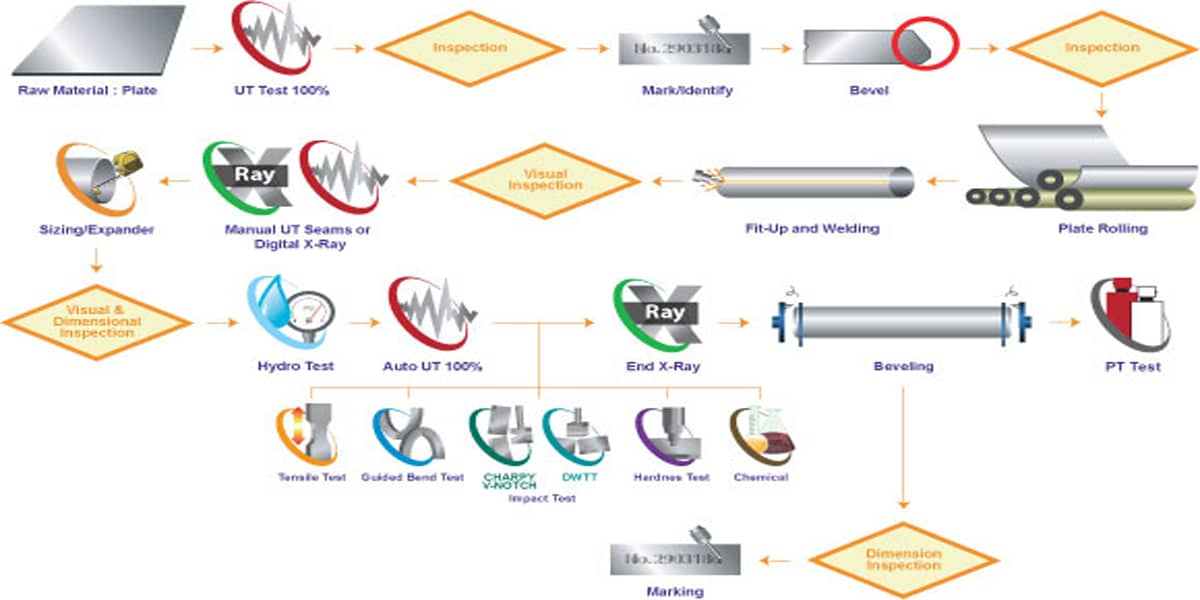
Manufacturing Process of ASTM A671 Steel Pipes
ASTM A671 steel pipes are manufactured using the Electric-Fusion Welding (EFW) process. This method ensures the strength and reliability of the pipes under low-temperature and high-pressure conditions. Below is a step-by-step explanation of the manufacturing process:
1. Raw Material Preparation
Steel Plate Selection
ASTM A671 steel pipes are made from carbon steel or low-alloy steel plates, with materials selected based on the requirements of the specific application. Grades such as ASTM A671 Grade CC60, CC65, and CC70 are chosen depending on pressure and temperature needs.
Quality Inspection
The steel plates undergo strict chemical composition analysis and mechanical property testing to ensure they meet the requirements for low-temperature or high-pressure use.
2. Plate Forming:
The steel plates are cut into specific dimensions and then bent into the desired circular or sectional shape using a rolling machine, ensuring proper alignment of the edges.
3. Electric-Fusion Welding (EFW)
Welding Process
The edges of the steel plates are fused together using electric-fusion welding. This process uses electric current to heat the welding area, ensuring that the weld seam has strength equivalent to the base metal.
Weld Seam Inspection
After welding, the seam undergoes 100% non-destructive testing (e.g., ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspection) to detect cracks, pores, or other defects.
4. Heat Treatment (Optional)
To improve the mechanical properties of the weld seam, some ASTM A671 steel pipes undergo Post-Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT).
Heat treatment eliminates residual stresses generated during welding and enhances the toughness and fatigue resistance of the material.
5. Pipe Sizing and Calibration
After welding, the pipes are shaped and calibrated to ensure that their diameter, roundness, and wall thickness meet the specified requirements.
The pipes are also cut to the required lengths, and the ends are machined as necessary.
6. Inspection and Testing
Mechanical Property Testing
Tests such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and hardness are performed to ensure compliance with ASTM A671 Class specifications.
Pressure Testing
Hydrostatic or pneumatic testing is conducted to verify the pipe’s strength and seal integrity under high-pressure conditions.
Non-Destructive Examination
Non-destructive testing methods, such as magnetic particle testing and ultrasonic testing, are applied to ensure the pipes are free from defects.
7. Surface Treatment and Marking
Surface Treatment
The pipe surfaces are treated to enhance corrosion resistance, typically through painting, galvanizing, or sandblasting.
Marking
Specifications, including ASTM A671, Grade, and Class, are marked on the pipes for identification and traceability.

Grades and Classes of ASTM A671
ASTM A671 steel pipes are categorized into Grades and Classes to meet diverse requirements for pressure, temperature, and specific operating conditions. These classifications provide flexibility, making them suitable for applications ranging from low-temperature systems to high-pressure environments.
Grades: The grade of ASTM A671 pipes is determined by the type of steel plate used. The most common grades are:
1. Grade: Each grade has specific yield strength and tensile strength values, which determine its suitability for various applications.
CC60: Low strength, suitable for low-pressure and low-temperature environments. Liquid transport, low-pressure pipelines
CC65: Medium strength, suitable for moderate pressure or temperature systems. Chemical pipelines, storage systems
CC70: Highest strength, suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments. Boilers, high-pressure pipelines, nuclear systems
2. Classes: The class of ASTM A671 pipes is based on the post-weld treatment and testing requirements. Common classes include:
Class 10: Welds are not heat-treated but are subjected to non-destructive testing (NDT). Suitable for general industrial use.
Class 20: Welds undergo localized heat treatment (typically post-weld heat treatment) to improve the weld area’s properties.
Class 30: Pipes are heat-treated as a whole (e.g., annealed or normalized) to enhance overall mechanical properties and durability.
Class 40: Welds are not heat-treated but undergo 100% radiographic inspection for high-reliability applications.
Class 50: Welds are heat-treated and subjected to 100% radiographic inspection, ideal for high-pressure and critical applications.
The choice of class depends on the specific application and the required quality of the welded joints. For example, Class 30 and Class 50 are often used in high-pressure, high-temperature, or critical systems.
Industry Applications of ASTM A671 Steel Pipes
ASTM A671 steel pipes are widely used across various industries due to their excellent strength, durability, and suitability for both low and high-pressure systems. The combination of electric-fusion welding and heat treatment ensures their reliability under demanding conditions, making them ideal for applications requiring durability, toughness, and resistance to extreme temperatures or pressures.
1. Oil and Gas Industry
Pipelines: Used for transporting crude oil, natural gas, and other petroleum products.
Refinery Systems: Essential for process piping in refineries where high-pressure and high-temperature conditions are common.
Offshore Platforms: Withstand harsh marine environments, ensuring durability and performance.
2. Chemical and Petrochemical Industry
Process Pipelines: Suitable for carrying chemicals under corrosive and high-pressure conditions.
Storage Tanks: Used in systems that connect storage tanks and processing units.
Reactor Piping: Handles extreme temperatures and pressures in chemical reactions.
3. Power Generation
Boiler Piping: Common in power plants for high-temperature steam and water transportation.
Nuclear Systems: Used in nuclear power plants due to their ability to maintain structural integrity under critical conditions.
4. Industrial Applications
Heating Systems: Utilized in industrial heating and cooling systems for fluid transport.
Structural Uses: Employed in the construction of durable frameworks and supports.
ASTM A671 steel pipes in certain applications
High Pressure and Temperature Resistance: ASTM A671 steel pipes are designed to withstand high pressure and temperatures, making them suitable for industries like oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing.
Corrosion Resistance: Due to their alloy composition, these pipes are resistant to corrosion, which is crucial in harsh environments such as marine, chemical, and wastewater treatment industries.
Weldability: These pipes have excellent welding properties, ensuring that they can be easily joined to form large, robust pipeline systems, a common requirement in infrastructure projects.
Durability: ASTM A671 steel pipes offer long-term durability and strength under mechanical stress, which is vital for ensuring the reliability and safety of high-pressure systems.
How to Select the Appropriate ASTM A671 Steel Pipe
1. Pipe Size and Specifications
Pipe Diameter: Choose the appropriate pipe diameter based on the required flow rate and application. Larger diameters are suitable for high-flow applications, while smaller diameters are used for lower flow systems.
Wall Thickness: Select the correct wall thickness based on the pressure requirements. Thicker walls are needed for higher pressure and external impact resistance.
2. Operating Environment
Temperature Requirements: For applications requiring resistance to high or low temperatures, the temperature tolerance of the ASTM A671 steel pipe is critical. Select the pipe that can withstand the maximum and minimum temperatures of the working environment.
Corrosive Environments: If the pipe will be used for transporting corrosive substances (such as chemicals or seawater), choose a pipe with strong corrosion resistance. ASTM A671 steel pipes typically offer good resistance to corrosion due to their alloy composition.
3. Pressure Rating: Select a steel pipe based on the required pressure rating. ASTM A671 pipes are suitable for high-pressure transport systems, commonly used in oil and gas, chemical, nuclear, and other high-demand industries, ensuring safety and reliability under high-pressure conditions.
4. Weldability: ASTM A671 steel pipes are often used in systems that require welding. It is essential to choose a pipe with excellent weldability to ensure reliable installation of the pipeline.
5. Certifications and Quality Assurance: Ensure that the steel pipe complies with ASTM A671 standards and check for relevant quality certifications (e.g., ISO certification). This will help ensure that the steel pipe meets the necessary quality standards for the project.
6. Industry-Specific Applications
Select the appropriate type of steel pipe based on the specific industry:
Oil and Gas: Pipes for high-pressure, high-temperature, and corrosive environments.
Chemical Industry: Pipes for transporting chemicals, particularly those with excellent corrosion resistance.
Power Industry: Pipes for cooling systems and high-temperature, high-pressure conditions.
7. Budget and Cost: Cost is an important factor when selecting steel pipes. Choose pipes with the appropriate wall thickness and specifications while keeping within the project’s budget.
8. Expertise and Experience: Suppliers with extensive experience in the industry often have a deep understanding of material properties, application requirements, and project-specific needs. They can provide valuable insights into which pipe specifications are best suited for particular environments or projects.
The Future Development Trends of ASTM A671 Steel Pipes
The future development trends of ASTM A671 steel pipes are shaped by advancements in technology, evolving industry needs, and environmental considerations. Here are some key trends expected to influence the future of ASTM A671 steel pipes:
1. Higher Strength and Durability
Advancements in Material Science: As industries push for stronger and more durable materials, we can expect continued improvements in the steel composition of ASTM A671 pipes. These pipes will be engineered to withstand even higher pressures, temperatures, and corrosive environments, particularly in oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing industries.
Enhanced Mechanical Properties: Research into new alloys and heat treatment processes could lead to ASTM A671 pipes with improved tensile strength, resistance to fatigue, and longer operational lifespans.
2. Improved Corrosion Resistance
Coatings and Surface Treatments: As industries become more focused on sustainability and cost-efficiency, there will be a growing demand for ASTM A671 pipes with advanced corrosion-resistant coatings. This would extend the lifespan of the pipes, reduce maintenance costs, and improve their performance in challenging environments (e.g., offshore platforms, wastewater systems, and chemical plants).
Self-Healing Materials: Emerging technologies might lead to the development of self-healing coatings or pipe materials that can repair themselves when damaged, thus improving long-term durability.
3. Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Manufacturing
Recycling and Circular Economy: The steel industry is increasingly focusing on sustainability. Future ASTM A671 pipes may be produced using more environmentally friendly processes, such as increasing the use of recycled steel in manufacturing, reducing carbon emissions, and optimizing energy consumption during production.
Lower Environmental Impact: The development of more eco-friendly manufacturing techniques will reduce the carbon footprint of ASTM A671 steel pipes, aligning with global sustainability goals and environmental regulations.
4. Advanced Manufacturing and Automation
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing: The integration of 3D printing technology could allow for more precise and customizable ASTM A671 steel pipes, particularly in specialized applications where traditional manufacturing methods are not cost-effective or feasible. This could also reduce material waste and enable on-demand production.
Automation in Production: More automated and digitalized manufacturing processes will improve the consistency and quality control of ASTM A671 pipes, reducing defects and ensuring that pipes meet exact specifications for high-demand applications.
5. Smarter Pipes with Monitoring Capabilities
Smart Pipelines: With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), ASTM A671 steel pipes may incorporate sensors to monitor factors such as pressure, temperature, flow rates, and corrosion levels in real-time. This would enable predictive maintenance, reduce downtime, and improve overall safety by providing early warnings of potential issues.
Data Integration: The integration of data from smart pipelines into broader infrastructure management systems will help optimize performance and ensure the longevity of the entire pipeline network.
6. Customization and Specialized Applications
Tailored Solutions for Specific Industries: As industries evolve, there will be a growing need for customized ASTM A671 steel pipes designed to meet specific requirements, such as unique size dimensions, material grades, or specialized coatings. This trend will likely increase in sectors like nuclear energy, aerospace, and advanced chemical manufacturing.
Integration with Renewable Energy Systems: With the growing importance of renewable energy sources, ASTM A671 pipes may be adapted for use in systems like geothermal energy or hydrogen transport pipelines, which require materials with specific resistance to high pressure, temperature, and chemical exposure.
7. Global Supply Chain Optimization
Faster Production and Delivery: As industries continue to globalize, there will be an emphasis on optimizing the supply chain for ASTM A671 steel pipes, ensuring that they are produced and delivered faster and more cost-effectively. The use of digital platforms for supply chain management and tracking will be crucial.
Localized Production: In response to disruptions like those seen during the COVID-19 pandemic, there may be an increase in localized manufacturing of ASTM A671 pipes to reduce dependence on global supply chains and ensure greater resilience in critical industries.
By exploring the development trends, applications, and future outlook of ASTM A671 steel pipes, it’s clear that this material plays an indispensable role across various industries. With technological advancements, increasing environmental demands, and diversified industry applications, ASTM A671 steel pipes will continue to be a key component in modern infrastructure. Whether in oil and gas, chemical, or power sectors, their exceptional resistance to pressure, temperature, and corrosion makes them a critical choice.
If you’re interested in the future developments of ASTM A671 steel pipes or related industries, feel free to like and follow us for more in-depth analyses and the latest trends. Let’s explore more industry insights together and embrace a smarter, more sustainable future!



