- 1. Overview of AS 1163 and AS/NZS 1163 Standards
- 2. Specifications and Dimensions of AS 1163 and AS/NZS 1163 Steel Pipes
- 3. Performance Characteristics of AS 1163 Steel Pipes
- 4. Industry Applications of AS 1163 Steel Pipes
- 5. How to Choose the Right AS 1163 Steel Pipe
- 6. Future Trends of AS 1163 Steel Pipes
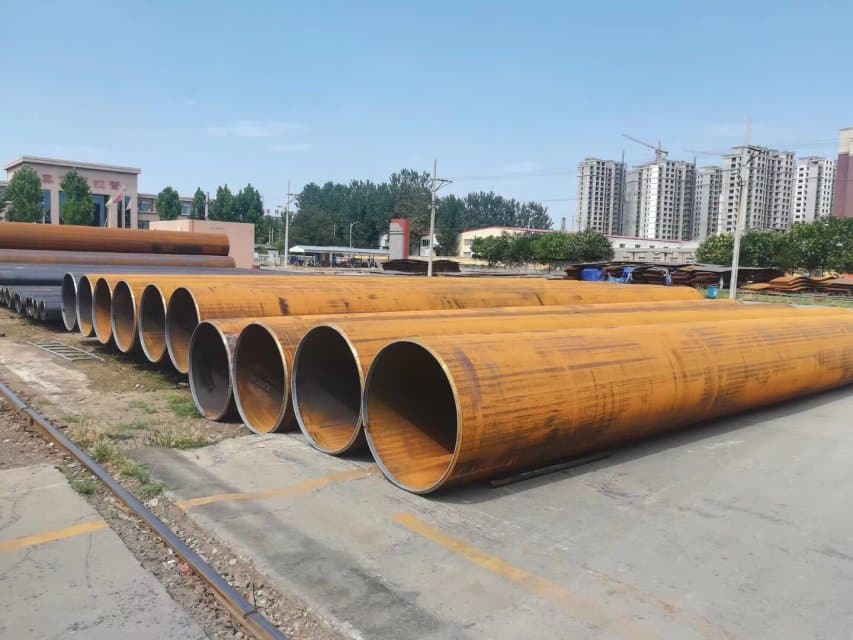
In the global steel pipe industry, the AS 1163 and AS/NZS 1163 standards are crucial for defining the specifications and performance requirements of structural steel pipes. AS 1163 is developed by the Australian Standards Association, while AS/NZS 1163 is a joint standard published by Australia and New Zealand. These standards ensure the quality, strength, and safety of steel pipe products, which are widely used in construction, engineering, and infrastructure projects. Understanding the details of AS 1163 and AS/NZS 1163 is essential for making informed decisions when selecting and applying these steel pipes, ensuring optimal results in engineering projects!

Overview of AS 1163 and AS/NZS 1163 Standards
AS 1163 and AS/NZS 1163 are two crucial standards for steel pipe products, developed by standard organizations in Australia and New Zealand. These standards primarily define the design and quality requirements for structural steel pipes, ensuring the safety, durability, and suitability of the pipes. While the two standards are quite similar, they differ in regional applicability, with AS 1163 applying only in Australia, while AS/NZS 1163 is a joint standard for both Australia and New Zealand.
1. AS 1163 Standard
AS 1163, developed by the Australian Standards Association, focuses on structural steel pipes used in various mechanical, construction, and infrastructure applications. The standard specifies the chemical composition, mechanical properties, dimensions, tolerances, and other quality requirements for steel pipes. AS 1163 steel pipes are commonly used in steel structures, frames, bridges, and other critical applications.
2. AS/NZS 1163 Standard:
AS/NZS 1163 is a joint standard published by Australia and New Zealand, with content similar to AS 1163 but broader in scope to meet the needs of both countries. The standard covers all aspects of steel pipes, including mechanical performance, welding requirements, testing methods, and ensures the products comply with strict quality control standards in both nations. It is widely used in construction, engineering, and other structural applications, with a strong emphasis on safety and durability.
Key Differences
Regional Applicability: AS 1163 applies only to Australia, while AS/NZS 1163 is applicable to both Australia and New Zealand.
Standard Content: While the requirements and specifications are highly similar, AS/NZS 1163 may include adjustments and additions specific to the New Zealand market.
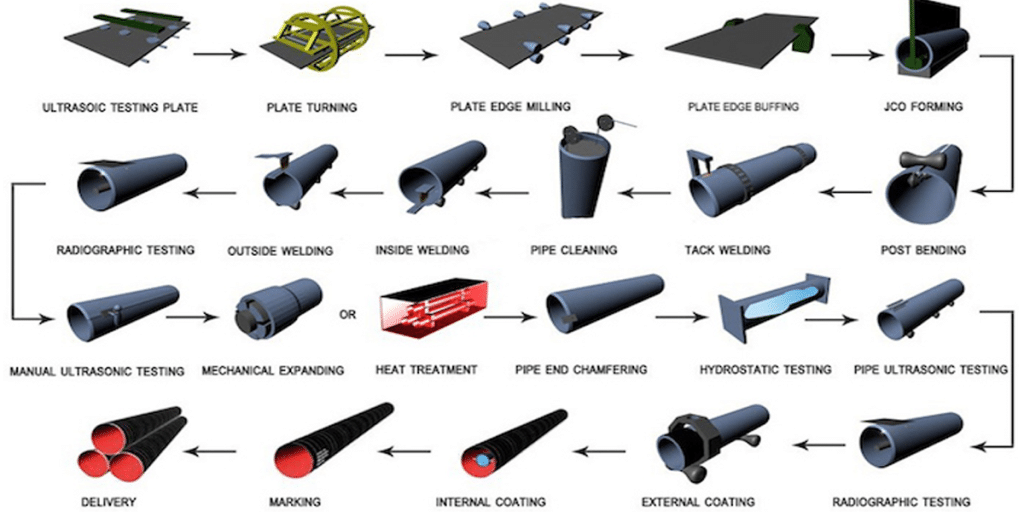
Specifications and Dimensions of AS 1163 and AS/NZS 1163 Steel Pipes
The AS 1163 and AS/NZS 1163 standards define the specifications, dimensions, tolerances, and other requirements for steel pipes, ensuring they have sufficient strength and reliability for various engineering applications. Below are the key specifications and dimensions under these standards:
1. Steel Pipe Specifications
The specifications for steel pipes under AS 1163 and AS/NZS 1163 typically cover the following aspects:
Pipe Types: Steel pipes are available in different types, primarily round, square, and rectangular pipes.
Material Grade: Steel pipes are made from various grades of steel, typically high-strength low-alloy steel or carbon steel, meeting the relevant mechanical performance requirements.
Wall Thickness: The wall thickness of steel pipes ranges from 1.6mm to 16mm, depending on the pipe diameter and intended use.
Pipe Outer Diameter (OD) and Inner Diameter (ID): The outer diameter typically ranges from 20mm to 400mm or more. The inner diameter is proportionate to the outer diameter and meets the required specifications for engineering applications.
2. Dimensional Tolerances
AS 1163 and AS/NZS 1163 standards provide clear tolerance requirements for the dimensions of steel pipes, ensuring the quality and precision of the pipes. Common dimensional tolerances include:
Outer Diameter Tolerance: The tolerance for outer diameter is typically ±1mm to ±2mm, depending on the pipe diameter.
Wall Thickness Tolerance: Wall thickness tolerance typically ranges from ±0.2mm to ±0.5mm, varying depending on the pipe size and intended application.
3. Length Requirements
Steel pipes are usually custom-made according to customer needs and engineering specifications. Standard lengths are typically 6 meters and 12 meters, but special lengths can be manufactured based on customer requirements.
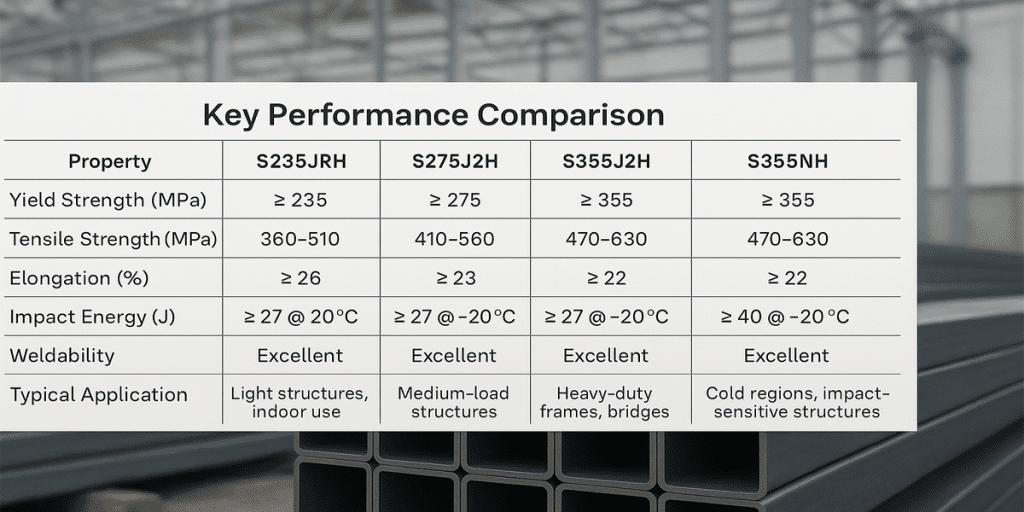
4. Mechanical Properties of Steel Pipes
Tensile Strength: AS 1163 and AS/NZS 1163 standards require steel pipes to have a tensile strength between 350 MPa and 550 MPa, depending on the type of pipe and its intended application.
Yield Strength: The yield strength typically ranges from 250 MPa to 350 MPa, ensuring that the pipe maintains sufficient stability under stress.
Weldability: The weldability of steel pipes is another key requirement in the standards, ensuring that the pipes can be welded without cracks or other defects.
5. Surface Quality Requirements
AS 1163 and AS/NZS 1163 also specify surface quality requirements for steel pipes. The pipes must be free from significant defects such as cracks, holes, or oxide layers, ensuring their safety and durability during use.
Performance Characteristics of AS 1163 Steel Pipes
AS 1163 steel pipes are high-strength pipes designed for structural purposes, widely used in construction, bridges, infrastructure, and other engineering applications. According to the AS 1163 standard, steel pipes are required to have excellent mechanical properties and meet the demands of various practical applications. Here are the main performance characteristics of AS 1163 steel pipes:
1. High Strength: A key feature of AS 1163 steel pipes is their high strength. The standard specifies tensile strength typically ranging from 350 MPa to 550 MPa, and yield strength usually falls between 250 MPa to 350 MPa. This allows the pipes to withstand significant loads and stress, making them ideal for load-bearing structures and seismic designs.
2. Excellent Weldability: AS 1163 steel pipes offer excellent weldability, allowing them to be welded during production and construction processes. These pipes do not develop cracks or other defects during welding, ensuring that the welded joints have the same strength as the pipe itself. Weldability is a crucial factor in applications where large-scale steel structures are involved.
3. Corrosion Resistance: AS 1163 steel pipes have good corrosion resistance, making them suitable for use in various environmental conditions. While the standard does not specifically address corrosion protection methods, the material and surface treatments can provide enhanced corrosion resistance, extending the lifespan of the pipes in challenging conditions.
4. Good Formability: AS 1163 steel pipes are made from high-quality steel, offering good formability, making them easy to cold bend, hot bend, or cut during production. This flexibility in processing allows the pipes to be customized in various shapes and sizes to meet the needs of different structural applications.
5. Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerances: AS 1163 standard requires strict dimensional accuracy and tolerance for steel pipes, ensuring precise fitting during installation and application. The tolerances for outer diameter and wall thickness ensure uniformity and consistency, allowing the pipes to integrate seamlessly with other building and structural materials.
6. Safety and Durability: Thanks to their high strength and excellent structural performance, AS 1163 steel pipes maintain stability over long periods of use, particularly under external forces, vibrations, and extreme environmental conditions. Their durability makes them an ideal choice for long-term applications in construction, bridges, and energy sectors.

Industry Applications of AS 1163 Steel Pipes
AS 1163 steel pipes, with their high strength, excellent weldability, and durability, are widely used in various industries. Below are the key sectors where AS 1163 steel pipes are commonly applied:
1. Construction Industry: In the construction industry, AS 1163 steel pipes are often used for structural support and framework construction. The high strength and good weldability of the pipes make them essential for load-bearing walls, frame columns, beams, and other structural components. They can withstand significant loads and maintain structural stability in harsh weather and environmental conditions.
2. Bridge Construction: AS 1163 steel pipes are widely used in bridge construction, particularly in the support structures of steel bridges. Their high tensile strength and yield strength allow them to effectively bear the pressures and stresses in bridge structures, ensuring safety and durability. Steel pipes are used in bridge support columns, foundations, as well as transverse and longitudinal connecting components.
3. Energy Sector: In the energy sector, especially in the transportation and storage of oil, gas, and mineral energy, AS 1163 steel pipes are extensively used in pipelines and storage facilities. The pipes’ strength and corrosion resistance allow them to safely operate under high-pressure conditions, ensuring the efficient transport of energy. Additionally, steel pipes are used for structural support in oil platforms, mining facilities, and energy extraction equipment.
4. Infrastructure Development: AS 1163 steel pipes are also widely applied in infrastructure development, particularly in public utilities, road construction, and underground piping systems. Due to their excellent formability and dimensional accuracy, steel pipes can be customized to meet various application needs, such as water pipes, drainage pipelines, and communication line supports.
5. Transportation Industry: In the transportation industry, AS 1163 steel pipes are used to manufacture support structures for railways, roads, and other transportation facilities. The high strength and stability of the pipes allow them to endure long-term loads from road and rail traffic. Steel pipes are also widely used in the construction of vehicle frames, tracks, and station buildings.
6. Industrial Manufacturing: AS 1163 steel pipes have significant applications in industrial manufacturing, particularly in mechanical manufacturing and equipment support structures. Steel pipes are used in machinery structures, equipment frames, and transmission pipelines, providing the necessary support to ensure stable operation of industrial equipment.
7. Agriculture and Water Conservancy: In agriculture and water conservancy projects, AS 1163 steel pipes are used for irrigation systems, water facility supports, irrigation pipelines, and drainage facilities. The corrosion resistance and strength of the pipes ensure these facilities can withstand water pressure and environmental influences over time.
How to Choose the Right AS 1163 Steel Pipe
Selecting the appropriate AS 1163 steel pipe is crucial to ensuring the structural safety, durability, and cost-effectiveness of a project. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing the right AS 1163 steel pipe:
1. Identify Application Requirements
First, clarify the specific use and application of the steel pipe. Different applications require different levels of strength, corrosion resistance, and other performance characteristics. For example:
Construction and Structural Applications: For use in building frames or support structures, ensure that the steel pipe has sufficient tensile strength and yield strength.
Bridge Construction: For bridges and other heavy-load-bearing structures, select high-strength, corrosion-resistant pipes.
Energy and Chemical Industries: In high-pressure or corrosive environments, the pipe’s corrosion resistance and pressure tolerance are critical.
2. Select the Appropriate Material and Grade
According to the AS 1163 standard, steel pipes are typically made from high-strength low-alloy steel or carbon steel. Different material grades are suited to different application needs, such as:
Grade C: Suitable for general construction and structural use.
Grade D: Ideal for structures requiring higher strength.When selecting, choose the material grade based on the specific load requirements and usage conditions.
3. Consider the Size and Specifications of the Pipe
Choosing the right pipe size is crucial and involves the following considerations:
Outer Diameter and Wall Thickness: These factors impact the pipe’s load-bearing capacity. Select the size based on engineering design and specific load-bearing needs. Standard pipe lengths are usually 6 meters or 12 meters, but custom lengths can be provided.
Tolerances: The AS 1163 standard specifies strict dimensional tolerance requirements, ensuring precise fit during installation. Ensure that the pipe’s outer diameter, tolerances, and wall thickness meet project specifications.
4. Evaluate the Pipe’s Weldability
AS 1163 steel pipes have specific requirements for weldability. When selecting, ensure that the pipe can be easily welded and that the welded joints maintain the pipe’s strength. This is especially important in large-scale structures or load-bearing systems where weld integrity is essential.
5. Corrosion Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Corrosion resistance is a key consideration for many applications, particularly in harsh environments. When choosing steel pipes, consider the following factors:
Surface Treatment: Some projects may require corrosion-resistant coatings or hot-dip galvanization to enhance the pipe’s resistance to corrosion.
Environmental Conditions: If the pipes will be used in humid, chemically corrosive, or marine environments, consider selecting pipes with stronger corrosion resistance.
6. Compliance and Standard Certification
Ensure that the selected steel pipes fully comply with the AS 1163 standard and carry the appropriate quality certifications. This ensures that the pipes will meet safety and reliability requirements during their service life.
7. Cost and Supply Considerations
Lastly, consider budget constraints and the supply capabilities of the manufacturer. Aim for steel pipes that offer good value for money while also considering supply timelines and transportation logistics to ensure that the project proceeds on schedule.
Future Trends of AS 1163 Steel Pipes
As industries such as construction, energy, and infrastructure continue to evolve, the demand for AS 1163 steel pipes is also changing. To meet these shifts, the steel pipe industry is moving in several key directions. Here are some future trends for AS 1163 steel pipes:
1. High Strength and Lightweight Design: In the future, AS 1163 steel pipes will increasingly use high-strength materials to improve load-bearing capacity while reducing the amount of material used, achieving lightweight design. This trend is particularly applicable to areas like bridge construction, building frameworks, and energy facilities that require substantial load-bearing. High-strength steel pipes can lower overall project costs and resource consumption while ensuring structural safety.
2. Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: With rising environmental standards, especially for applications in harsh conditions such as marine and chemical environments, corrosion resistance will become more critical. In the future, AS 1163 steel pipes will adopt advanced anti-corrosion technologies, such as hot-dip galvanizing, coating technologies, and special alloy compositions to improve the pipe’s durability and stability in harsh environments. This will be particularly beneficial for industries like oil, natural gas, and mining.
3. Green Manufacturing and Sustainability: Environmental protection and sustainability have become global priorities, and the steel pipe industry will also move toward greener production. In the future, AS 1163 steel pipe manufacturing will focus on energy conservation, waste reduction, and the use of recyclable materials. The extended lifespan and higher recycling rates of steel pipes will help reduce resource waste and promote green building and sustainable infrastructure.
4. Multifunctionality and Composite Materials: To improve steel pipe applicability in various complex environments, there may be a trend toward using composite or multifunctional steel pipes in the future. For example, combining high-strength steel with materials such as plastic or ceramics can create pipes with enhanced pressure resistance, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature durability. These composite materials can be used in more demanding industrial environments such as those with high temperatures, high pressure, or strong corrosive conditions.
In conclusion, AS 1163 and AS/NZS 1163 steel pipes are integral to the future of structural and industrial applications. As we move toward more advanced, high-strength, and environmentally sustainable solutions, these standards will continue to play a key role in ensuring the safety, durability, and performance of steel pipes. The ongoing evolution of these standards reflects the industry’s commitment to meeting the growing demands of diverse applications while addressing environmental challenges and technological advancements.
We encourage you to stay updated on the latest developments in AS 1163 and AS/NZS 1163 steel pipes. For more valuable insights and to explore how these standards can benefit your projects, follow our official account. Stay informed, and let us support your journey toward high-quality and reliable steel pipe solutions. Thank you for reading!