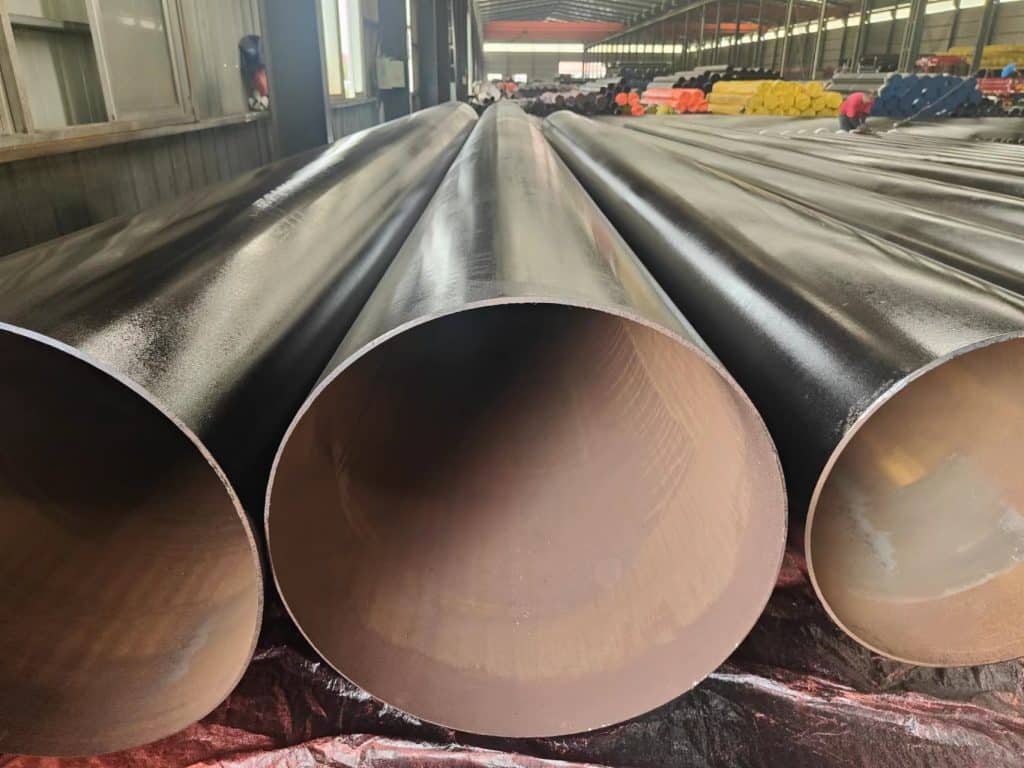
With the global construction industry continuing to grow amidst increasing competition, material selection and cost control have become key factors for the success of any project. In the current economic climate, construction companies and engineers face the dual challenges of fluctuating raw material prices and increasingly stringent environmental regulations. Finding ways to maintain building quality while reducing costs and improving construction efficiency has become a pressing issue. Against this backdrop, ASTM A53 steel pipes have emerged as a popular choice in the construction industry, thanks to their excellent corrosion resistance, structural stability, and relatively low cost. From supporting high-rise buildings to laying underground pipeline systems, ASTM A53 steel pipes are widely used across various construction projects, helping the industry tackle these market challenges. This article will explore the broad applications of ASTM A53 steel pipes in the construction sector and how they contribute to reducing costs, enhancing safety, and promoting sustainability!
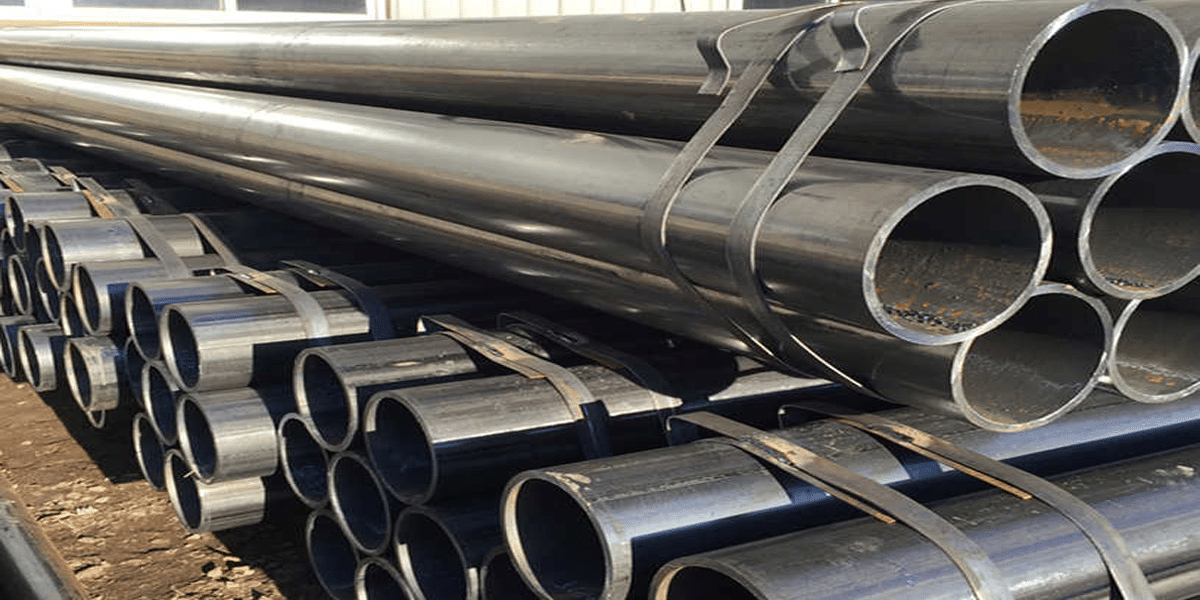

Overview of ASTM A53 Steel Pipes
What is ASTM A53 Steel Pipe?
ASTM A53 steel pipe is a specification issued by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) for carbon steel pipes. These pipes are commonly used in construction, oil and gas, water systems, and various industrial applications. ASTM A53 steel pipes are essential in fluid transportation, structural support in buildings, and other critical applications due to their excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and adaptability.
1. ASTM A53 Steel Pipe Standards and Types
ASTM A53 Steel Pipe Standards:
ASTM A53 is a standard specification for seamless and welded carbon steel pipes. The standard provides requirements for pipe dimensions, wall thickness, strength, material composition, and quality control. The specification is classified under ASTM A53/A53M.
Types of ASTM A53 Steel Pipes:
A53-A: Low-carbon steel pipes, suitable for applications with lower mechanical performance requirements.
A53-B: Higher-strength carbon steel pipes, commonly used in oil and gas pipelines, construction, and other high-strength applications.
ASTM A53 steel pipes are available in three types based on the manufacturing process:
Seamless Steel Pipes: Manufactured without a welded seam, these pipes are ideal for applications that require higher pressure tolerance.
Electric Resistance Welded (ERW) Steel Pipes: Made by welding the edges of the steel sheets together, commonly used for lower-pressure fluid transportation.
Spiral Welded Steel Pipes (SAW): Typically used for large-diameter and thick-walled pipes.
2. Basic Characteristics of ASTM A53 Steel Pipe
Material: ASTM A53 steel pipes are made from high-quality carbon steel, offering good mechanical properties and adaptability to various environments.
Corrosion Resistance: These pipes provide excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for use in underground pipelines or environments with high moisture.
Pressure and Tensile Strength: ASTM A53 steel pipes have high compressive and tensile strength, ensuring stability under high-pressure and load-bearing conditions.
Wall Thickness: The pipes are available in various wall thicknesses, meeting the specific requirements of different engineering projects.
Wide Application: ASTM A53 steel pipes are widely used in construction, oil and gas, water supply systems, and industrial pipelines, among others.
3. Comparison with Other Pipe Materials
When compared with other common pipe materials, ASTM A53 steel pipes offer unique advantages but also have certain limitations.
Compared to Stainless Steel Pipes:
Advantages: ASTM A53 steel pipes are more cost-effective than stainless steel pipes, making them a better choice for projects with budget constraints.
Disadvantages: Stainless steel pipes have superior corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance, making them more durable in extreme environments.
Compared to PVC Pipes:
Advantages: ASTM A53 steel pipes offer higher mechanical strength than PVC pipes, making them suitable for systems that need to withstand greater pressure.
Disadvantages: PVC pipes are lighter and easier to handle, and in less aggressive environments (low-pressure and low-corrosion), PVC might be a more cost-effective solution.
Compared to Aluminum Pipes:
Advantages: ASTM A53 steel pipes have higher strength and can withstand greater external pressure compared to aluminum pipes.
Disadvantages: Aluminum pipes are lighter and have better corrosion resistance, making them more suitable for applications where weight and corrosion resistance are the primary concerns.
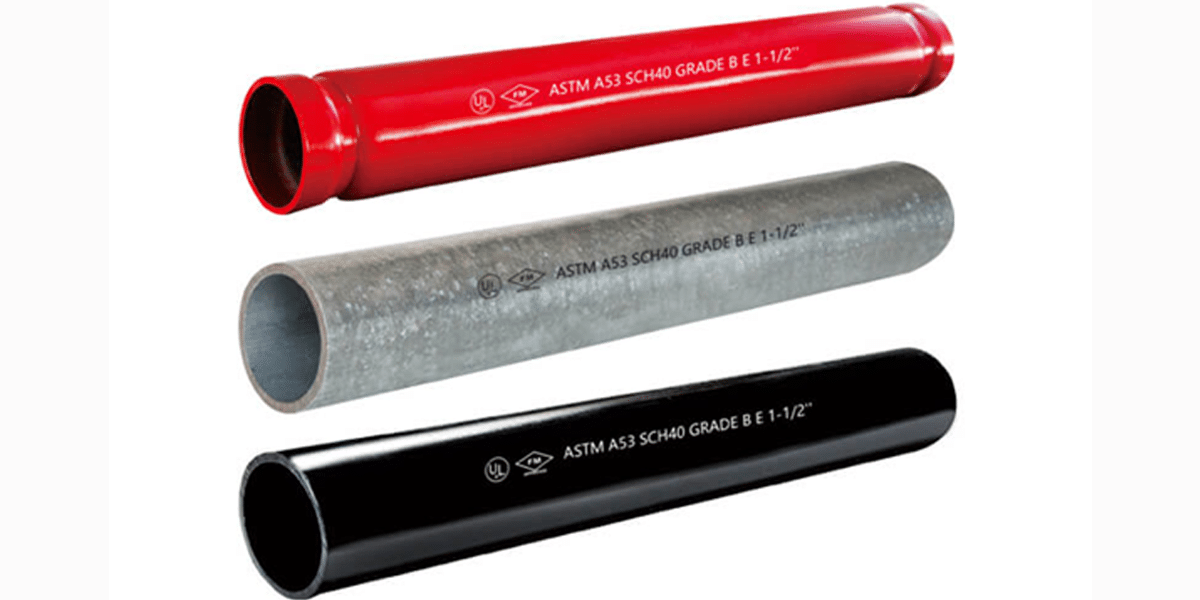

Application of ASTM A53 Steel Pipes in Building Pipeline Systems
ASTM A53 steel pipes, with their excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, are widely used in building pipeline systems. As a versatile carbon steel material, ASTM A53 steel pipes are commonly employed in water supply, gas supply, drainage, heating, and structural support within buildings. Their adaptability and durability make them an essential material in the construction industry, especially for projects requiring high pressure tolerance and resistance to harsh environments.
1. Water Supply Pipeline Systems: In building projects, water supply pipelines play a crucial role in delivering drinking and domestic water. The corrosion resistance and strength of ASTM A53 steel pipes make them an ideal choice for water supply systems. Particularly in large buildings, high-rise residential complexes, and commercial structures, ASTM A53 steel pipes are widely used. Their strength allows them to withstand high-pressure water flow, while maintaining stability in damp and corrosive environments.
2. Gas Supply Pipeline Systems: Another important application of ASTM A53 steel pipes in construction is in gas supply systems. Natural gas and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) require safe and efficient transportation through pipelines to building interiors. ASTM A53 steel pipes, with their good corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance, ensure long-term stability in changing external environments. They are especially suitable for high-safety gas supply systems, commonly used in oil and gas transport systems, providing excellent pressure endurance.
3. Drainage and Wastewater Pipeline Systems: Drainage systems are vital for the proper functioning of buildings, especially in large-scale projects. ASTM A53 steel pipes, with their corrosion resistance and high load-bearing capacity, are frequently used in building wastewater and stormwater drainage systems. The structural strength and durability of these pipes ensure they can withstand long-term pressure fluctuations and exposure to chemical substances, providing stable drainage for buildings.
4. HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) Systems: In building HVAC systems, ASTM A53 steel pipes are commonly used for transporting chilled water, steam, or hot water. Due to their excellent mechanical properties and thermal conductivity, ASTM A53 steel pipes effectively transfer heat and cold, maintaining the stable operation of HVAC systems. Furthermore, their resilience to extreme conditions makes them an ideal material for HVAC piping systems.
5. Structural Support and Framing Systems: In addition to their use in pipeline systems, ASTM A53 steel pipes are also widely used in building structural support and framing systems. In heavy-duty construction projects, ASTM A53 steel pipes are utilized as support columns, beams, and part of the structural framework to ensure the stability and safety of the building. Their high strength, durability, and low cost make them indispensable in building structures.
6. Fire Protection Systems: In some buildings, ASTM A53 steel pipes are used in fire water systems. These water pipes are designed to rapidly deliver water in the event of a fire emergency. Due to their high-temperature resistance and corrosion resistance, ASTM A53 steel pipes ensure the stability and reliability of the piping in fire protection systems. The strength of steel pipes also allows them to withstand water pressure and prevent leakage, enhancing the building’s fire safety.
Corrosion Resistance of ASTM A53 Steel Pipes
ASTM A53 steel pipes are widely used in construction, oil and gas transportation, and water treatment industries due to their excellent mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness. However, despite their durability, corrosion remains a significant challenge in their long-term performance. Corrosion can compromise structural integrity, shorten service life, and increase maintenance costs. To address this issue, various corrosion-resistant technologies have been developed to enhance the lifespan and reliability of ASTM A53 steel pipes.
1. Corrosion Issues and Challenges
During operation, ASTM A53 steel pipes are exposed to various corrosive environments. The main types of corrosion challenges include:
Moisture Corrosion: Water exposure, especially in humid or underground environments, can cause oxidation, leading to rust formation and structural weakening. This is a common issue in water supply, drainage, and gas pipelines.
Chemical Corrosion: In industries such as oil, gas, and chemical processing, steel pipes encounter corrosive substances like hydrogen sulfide and chlorides. These chemicals accelerate material degradation, causing cracks, leaks, and structural failure.
Electrochemical Corrosion: Also known as galvanic corrosion, this occurs when steel pipes come into contact with dissimilar metals or electrolytes, particularly in underground pipelines and offshore platforms. The electrical reactions lead to metal loss and corrosion damage.
Microbial Corrosion: In low-oxygen, damp environments, bacteria can attach to the steel surface and produce acidic byproducts that accelerate corrosion. This is a serious concern in wastewater and marine applications.
If left unaddressed, corrosion significantly reduces the operational safety and efficiency of pipeline systems, increasing maintenance and replacement costs.
2. Corrosion-Resistant Technologies
To mitigate corrosion risks, several effective protection technologies are applied to ASTM A53 steel pipes:
Galvanization (Zinc Coating): Hot-dip or electro-galvanization provides a protective zinc layer that prevents direct exposure of the steel to corrosive elements. This method is widely used in water supply and structural applications.
Protective Coatings: Applying anti-corrosion coatings such as epoxy resin, polyurethane, or fusion-bonded epoxy (FBE) can isolate the pipe surface from water, acids, and salts. This significantly enhances corrosion resistance, especially in aggressive industrial environments.
Cathodic Protection: This technique involves applying an external electrical current to the pipeline, making it act as a cathode to prevent corrosion. It is particularly effective for underground and offshore pipelines.
Alloying with Corrosion-Resistant Elements: Adding elements like chromium and nickel improves the corrosion resistance of ASTM A53 steel pipes, making them suitable for highly acidic or saline environments.
Corrosion Monitoring Systems: Advanced sensors and monitoring technologies can detect early signs of corrosion, allowing preventive maintenance before significant damage occurs.
3. Case Studies
Case 1: Corrosion Protection in Oil & Gas Transportation
In natural gas pipelines, ASTM A53 steel pipes are frequently exposed to hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) and chlorides, which can accelerate corrosion. A leading oil company implemented a dual-protection approach by using internal epoxy coatings and cathodic protection systems. This combination effectively minimized corrosion rates and extended the pipeline lifespan by over 20 years.
Case 2: Urban Water Supply Pipeline Solutions
Municipal water distribution systems often experience moisture-related corrosion. To combat this, many cities opt for hot-dip galvanized ASTM A53 pipes in their infrastructure. The zinc coating serves as a protective barrier, significantly reducing maintenance costs and ensuring long-term durability of the supply network.
How to Choose ASTM A53 Steel Pipes and the Installation Process?
1. How to Choose the Right ASTM A53 Steel Pipe
1.1 Understanding ASTM A53 Standards and Types
ASTM A53 steel pipes are classified based on the manufacturing process:
Type E (Electric Resistance Welded, ERW) – Used for mechanical and pressure applications, widely applied in structural and pipeline systems.
Type F (Furnace Welded, Continuous Welded) – Generally used for low-pressure transportation.
Type S (Seamless) – Ideal for high-pressure transportation such as oil and gas pipelines.
Additionally, ASTM A53 steel pipes are available in two grades:
Grade A – Lower strength, better ductility, suitable for light-duty applications.
Grade B – Higher strength, commonly used in industrial and structural projects.
1.2 Selecting the Right Corrosion Protection Coating
Black Steel Pipes – Uncoated, mainly used for gas pipelines and structural applications.
Galvanized Pipes – Coated with a layer of zinc to enhance corrosion resistance, commonly used in water supply systems.
FBE/Epoxy-Coated Pipes – Provides additional protection against chemicals, moisture, and harsh environments.
1.3 Choosing the Right Size and Wall Thickness: ASTM A53 steel pipes follow the Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) system, and selecting the correct pipe dimensions requires consideration of pressure rating, load-bearing requirements, and the type of transported fluid.
1.4 Ensuring Compliance with International Standards: Before procurement, ensure that ASTM A53 steel pipes comply with relevant industry standards such as API 5L, ASME, AWWA, or other specifications required for the project.
2. Installation and Construction Process
2.1 Pre-Installation Preparation
Conduct a site survey to assess terrain, load distribution, and environmental conditions.
Ensure compliance with safety guidelines to prevent accidents due to the weight and size of the pipes.
Prepare necessary tools such as pipe cutters, welding machines, and coating materials.
2.2 Pipe Cutting and Alignment
Use mechanical cutters or plasma cutting to ensure precision.
Align pipes correctly using pipe support structures to prevent bending or deformation.
For welding purposes, ensure proper beveling of pipe ends for a secure and efficient joint.
2.3 Welding and Jointing Methods
ERW pipes are typically connected using butt welding or flange connections.
Seamless pipes require high-strength welding techniques such as GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding) or SMAW (Shielded Metal Arc Welding).
Ensure smooth, leak-proof, and high-strength joints using appropriate welding techniques and post-weld inspections.
2.4 Corrosion Protection and Coating
Apply protective coatings such as galvanization, epoxy lining, or polyethylene wrapping, depending on environmental exposure.
Use cathodic protection (CP) for underground or marine applications to prevent electrochemical corrosion.
2.5 Testing and Quality Control
Perform hydrostatic pressure testing to check for leaks or structural weaknesses.
Use X-ray or ultrasonic testing (UT) to ensure the integrity of weld joints.
Ensure compliance with ASTM A53 and project-specific standards before putting the system into operation.
3. Quality Control and Inspection Standards
Ensuring the quality and reliability of ASTM A53 steel pipes is critical for their performance in construction, oil and gas transportation, water treatment, and industrial applications. The quality control and inspection of ASTM A53 steel pipes follow strict standards to meet safety, durability, and regulatory compliance requirements. Here are the key points we want to convey.
1. Compliance with International Standards
ASTM A53 steel pipes are manufactured to meet various global quality and safety standards, including:
API 5L – For oil and gas transportation pipelines.
ASME B36.10 & B36.19 – For industrial piping applications.
ISO 3183 – International standard for pipeline transportation systems.
AWWA C200 – For water transmission applications.
Compliance with these standards ensures that ASTM A53 pipes meet the requirements for strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for critical infrastructure projects worldwide.
2. Final Inspection and Certification
After all quality control and inspection procedures are completed, ASTM A53 steel pipes undergo final certification and documentation before shipping:
Third-party inspections may be conducted by agencies like SGS, BV, or TUV.
Each pipe is stamped with manufacturer details, ASTM A53 specification, grade, size, and heat number for traceability.
A Mill Test Certificate (MTC) is provided, detailing the test results and compliance with ASTM standards.

Future Trends of ASTM A53 Steel Pipes in the Construction Industry
As the construction industry continues to evolve, the demand for high-quality, durable, and cost-effective materials like ASTM A53 steel pipes is expected to grow. With advancements in technology, sustainability, and infrastructure development, ASTM A53 steel pipes are set to play a more significant role in modern construction. Below are the key trends shaping their future in the industry.
1. Increasing Demand for Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Materials
With global emphasis on green construction and sustainability, ASTM A53 steel pipes are being increasingly recognized for their recyclability and energy efficiency in manufacturing.
Recyclability: Steel is 100% recyclable, reducing waste and supporting circular economies.
Lower Carbon Footprint: Modern steel manufacturing processes focus on reducing emissions and energy consumption, making ASTM A53 pipes a more environmentally friendly choice.
Compliance with Green Building Certifications: ASTM A53 pipes contribute to achieving LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification, making them attractive for eco-conscious projects.
2. Advancements in Corrosion Resistance and Coating Technologies
Corrosion has always been a challenge in construction and pipeline applications, but new protective coatings and treatments are extending the lifespan of ASTM A53 steel pipes.
Galvanized ASTM A53 Pipes: Zinc coating enhances corrosion resistance, making them ideal for outdoor and underground applications.
Epoxy and Polyethylene Coatings: These coatings improve resistance to harsh environmental conditions, including humidity, saltwater exposure, and industrial chemicals.
Nano-Coating Technology: Emerging nanotechnology-based coatings offer self-healing and anti-corrosion properties, further improving durability.
3. Growth of Smart and Modular Construction
The modular construction market is rapidly expanding, requiring standardized and high-strength materials like ASTM A53 steel pipes.
Pre-Fabricated Structures: ASTM A53 pipes are widely used in modular buildings, pre-engineered steel structures, and temporary construction facilities.
Integration with Smart Infrastructure: With the rise of IoT (Internet of Things) in construction, ASTM A53 pipes can be embedded with smart sensors for real-time monitoring of pressure, temperature, and structural integrity.
Ease of Installation and Adaptability: ASTM A53 pipes are lightweight yet strong, making them easy to transport and install, which is crucial for fast-track construction projects.
ASTM A53 steel pipes, with their excellent mechanical properties, durability, and versatility, play a crucial role in the construction industry. As trends shift toward sustainability, smart infrastructure, and advanced building technologies, ASTM A53 steel pipes will continue to be a key component in modern construction. By enhancing material performance, improving corrosion resistance, and adapting to global market demands, ASTM A53 steel pipes will remain a reliable, efficient, and cost-effective solution, driving the industry toward a greener and more innovative future!







