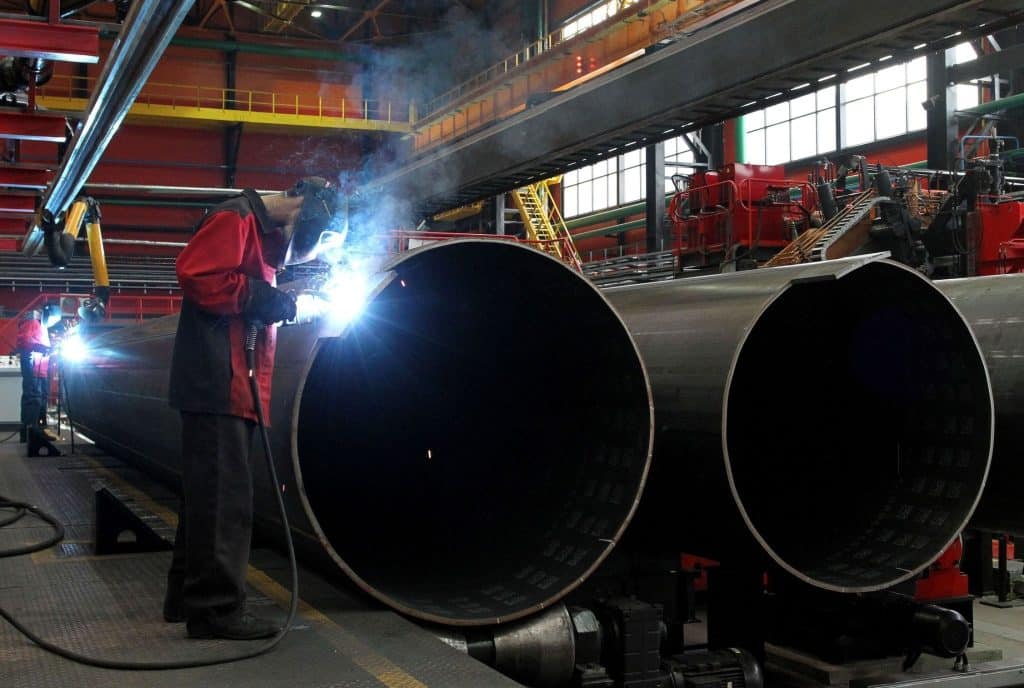
ASTM A53 Steel Pipe is one of the most widely recognized standards for carbon steel pipes, valued for its exceptional performance and broad applicability across various industries. Covering the specifications for A53 Carbon Steel, this standard sets strict requirements for mechanical properties, chemical composition, and manufacturing processes. Whether used in pipelines for transporting liquids and gases or as structural components in construction and infrastructure, Carbon Steel A53 stands out for its strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of ASTM A53, including its grade classifications, specifications, and diverse applications, offering insights into the significance of this essential standard!

Overview of the ASTM A53 Standard
Definition and Application Scope of ASTM A53
ASTM A53 is a carbon steel pipe standard established by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), widely used across industrial and engineering fields. This standard covers seamless and welded steel pipes designed for low-pressure transportation of liquids, gases, and other neutral media. Additionally, ASTM A53 Steel Pipe is commonly employed in construction and structural support applications. Based on its chemical composition and mechanical properties, ASTM A53 is classified into Grade A and Grade B, catering to varying strength and durability requirements.
Characteristics of A53 Carbon Steel Pipes
A53 Carbon Steel is renowned for its exceptional properties
High Strength: A53 pipes offer excellent tensile and compressive strength, making them suitable for demanding load-bearing applications.
Corrosion Resistance: With proper maintenance, Carbon Steel A53 exhibits resistance to oxidation and rust, ensuring a longer service life.
Ease of Fabrication: A53 pipes are highly weldable and formable, meeting diverse fabrication needs.
Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to alloy steels, A53 carbon steel is more affordable while maintaining excellent performance, making it a highly economical choice.
Comparison of ASTM A53 with Other Common Steel Pipe Standards
ASTM A106: Both cover seamless steel pipes, but A106 is specifically designed for high-temperature and high-pressure environments, while A53 is more suitable for low-pressure applications.
ASTM A500: A500 focuses on structural applications such as frames and trusses, whereas A53 is versatile, supporting both structural and transportation uses.
API 5L: API 5L is tailored for oil and gas pipelines with stricter size and pressure requirements, whereas A53 caters to more general industrial needs.
Grade Classification and Performance Comparison of ASTM A53
ASTM A53 steel pipes are classified into Grade A and Grade B based on their chemical composition, mechanical properties, and application scenarios. Below is a detailed comparison of their characteristics:
1. Chemical Composition Comparison: Grade B has a higher manganese content, which enhances its strength and hardness, making it more suitable for high-strength applications.
2. Mechanical Properties Comparison: Grade A offers better ductility, making it ideal for applications requiring more bending and forming, while Grade B’s higher strength makes it better suited for high-pressure or high-load conditions.
3. Application Scenarios
Grade A: Grade A is suitable for low-pressure, low-strength applications, such as pipelines for water, gas, or non-corrosive fluids. Its excellent ductility and formability make it ideal for welding and general processing.
Grade B: Grade B is commonly used in applications requiring higher strength and load-bearing capacity, such as pipelines for oil and gas transportation, industrial high-pressure systems, and critical structural components.
4. Performance Comparison with Other Standards
Compared to ASTM A106, ASTM A53 Grade A and Grade B are better suited for low-temperature, low-pressure environments, while A106 is designed for high-temperature and high-pressure conditions.
Compared to API 5L, A53 offers slightly lower strength but has advantages in terms of machinability and cost-effectiveness.

Classification and Production Types of ASTM A53
1. Classification Methods
(1) By Manufacturing Process:
Type E (Electric Resistance Welded, ERW):
Produced using electric resistance welding, featuring smooth and uniform weld seams. Commonly used for low-pressure pipelines transporting water, gas, or other fluids.
Type S (Seamless):
Manufactured using hot rolling or cold drawing, with higher strength and pressure resistance, suitable for high-pressure or high-temperature applications.
Type F (Furnace Welded):
Made using furnace welding, with lower strength, primarily for light-load or non-pressure applications.
(2) By Grade:
Grade A:
Lower strength but higher ductility, ideal for applications requiring bending and forming.
Grade B:
Higher strength, suitable for environments requiring greater pressure resistance or mechanical strength.
2. Production Types
(1) Seamless Steel Pipe:
Production Process: Made using piercing and hot rolling techniques, without any weld seams.
Features: High pressure and temperature resistance, stable mechanical properties.
Typical Applications: High-pressure boiler pipelines, oil, and gas pipelines.
(2) Electric Resistance Welded (ERW) Steel Pipe:
Production Process: Manufactured using electric resistance welding without any filler material, ensuring a compact weld seam.
Features: High production efficiency and lower cost, suitable for mass production.
Typical Applications: Transportation of water, gas, and petroleum in low-pressure systems.
(3) Furnace Welded Steel Pipe:
Production Process: Produced using furnace welding, mainly for non-pressure applications.
Features: Lower strength, suitable for lightweight structures or decorative purposes.
Typical Applications: Low-strength mechanical support or temporary pipelines.
3. Selection Criteria
Based on Pressure Requirements: Seamless pipes are preferred for high-pressure environments, while ERW pipes are suitable for low-pressure scenarios.
Based on Cost-Effectiveness: ERW pipes are more economical, making them ideal for large-scale projects.
Based on Environmental Conditions: For high-temperature or corrosive environments, Grade B seamless pipes are recommended.
Industry Applications of ASTM A53 Carbon Steel Pipes
1. Typical Applications of A53 Carbon Steel Pipes
Oil and Gas Industry
Used for the transportation of oil, gas, and other hydrocarbons in low-pressure pipelines.
Suitable for gathering lines, feeder lines, and distribution systems.
Seamless Type S pipes are often preferred for higher pressure pipelines.
Construction and Infrastructure
Utilized in structural applications such as columns, beams, and bracing.
Frequently used in scaffolding, temporary structures, and industrial framework due to their strength and cost-effectiveness.
Water Supply and Plumbing Systems
Commonly employed in pipelines for transporting water, sewage, and other liquids.
Furnace-welded (Type F) pipes can be used in non-critical, low-pressure plumbing systems.
Industrial and Mechanical Applications
Applied in machinery and equipment as process pipes or structural components.
Grade B is often selected for higher strength and reliability in demanding industrial conditions.
Steam and Heat Transfer Systems
Used in low-pressure steam pipelines and heat exchangers due to their heat resistance.
Seamless pipes are preferred for higher temperature and pressure applications.
2. Choice of Grade A vs. Grade B in Different Applications
Application Scenario
Low-pressure water or gas pipelines
Grade A: Suitable due to its higher ductility and ease of welding.
Grade B: May be used but typically not required.
High-pressure pipelines
Grade A: Not recommended due to lower strength.
Grade B: Ideal for withstanding high pressure and mechanical loads.
Structural components
Grade A: Adequate for light structures or temporary installations.
Grade B: Preferred for heavy-duty, permanent installations.
Heat transfer systems
Grade A: Suitable for moderate temperatures.
Grade B: Preferred for high-temperature, high-pressure systems.
3. Advantages of Carbon Steel A53
Versatility
ASTM A53 Steel Pipe is available in various types (Type E, S, and F) and grades (A and B), making it adaptable to a wide range of applications.
Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to alloy steel or other materials, A53 Carbon Steel offers excellent performance at a lower cost, reducing project expenses.
Durability and Strength
Grade B pipes provide high tensile and yield strength, making them suitable for demanding environments.
Ease of Fabrication
Carbon Steel A53 is highly weldable and formable, allowing for easy installation and customization on-site.
Corrosion Resistance
With proper maintenance and coatings, ASTM A53 Steel Pipe resists rust and oxidation, extending its lifespan in various environments.
Availability and Standardization
Widely manufactured and standardized globally, ensuring consistent quality and easy sourcing for industrial projects.

How to Choose the Right ASTM A53 Steel Pipe?
Selecting the appropriate ASTM A53 steel pipe requires a thorough evaluation of its intended application, operating environment, and cost-effectiveness. Below is a guide to help you make an informed decision by considering key factors.
1. Determine the Pipe’s Purpose
Different applications demand specific pipe types and grades. Choose based on the intended use:
Transporting low-pressure fluids (e.g., water, gas): Type E (Electric Resistance Welded) or Type F (Furnace Welded), Grade A for better ductility and cost-efficiency.
Transporting high-pressure fluids (e.g., oil, natural gas): Type S (Seamless), Grade B for superior strength and pressure resistance.
High-temperature environments (e.g., boiler pipelines): Type S (Seamless), Grade B for enhanced heat resistance.
Structural applications (e.g., supports, scaffolding): Type E or Type F, Grade A or B, depending on the load-bearing requirements.
2. Choose Based on Pressure Requirements
Low-pressure scenarios: Grade A is ideal due to its higher ductility, making it suitable for bending and welding.
High-pressure scenarios: Grade B is recommended for its higher tensile and yield strength.
3. Consider the Operating Environment
(1) Temperature Conditions:
For high-temperature environments, seamless pipes (Type S) are preferred for better thermal stability.
For moderate or low temperatures, Type E (ERW) pipes are more cost-effective.
(2) Corrosive Environments: For environments with high corrosion potential, use protective coatings or galvanized ASTM A53 steel pipes to ensure longevity.
4. Evaluate Cost-Effectiveness
For budget-sensitive projects with low pressure or temperature requirements, Type E or Type F pipes offer good performance at a lower cost.
For high-performance needs, seamless pipes (Type S), though more expensive, offer superior reliability and reduce maintenance costs over time.
5. Adhere to Industry Standards and Project Requirements
Verify if the project specifications mandate a specific type (Type E/S/F) or grade (Grade A/B).
Ensure compliance with ASTM A53 standards and relevant industry regulations.
6. Advantages of ASTM A53 Steel Pipes
Regardless of type or grade, A53 Carbon Steel Pipes offer several advantages:
Versatility: Applicable to a wide range of industrial uses, including low-pressure transportation, structural support, and high-pressure applications.
Durability: Particularly Grade B, known for its higher tensile and yield strength.
Ease of Fabrication: Carbon steel material is highly weldable and formable, simplifying installation.
Future Market Trends for ASTM A53 Steel Pipes
The demand for ASTM A53 steel pipes is expected to grow steadily in the coming years, driven by global infrastructure development and the ongoing transformation of the energy sector. Below is an analysis of future trends based on industry drivers, technological advancements, regional market demand, and sustainability initiatives.
1. Industry Drivers
Infrastructure Development
Governments worldwide are heavily investing in infrastructure projects, including urban pipelines, transportation networks, and energy transmission systems, directly boosting the demand for ASTM A53 Steel Pipes.
In regions like Asia-Pacific and the Middle East, the market for pipeline materials is anticipated to see robust growth.
Energy Transition and Pipeline Demand
As natural gas becomes a significant component of the global clean energy transition, the demand for pipelines suited for low- and medium-pressure gas transport is expected to increase. ASTM A53 pipes are ideal for these applications.
The growing interest in hydrogen energy may also create niche opportunities for ASTM A53 pipes in low-pressure hydrogen transmission.
2. Technological Advancements and Product Enhancements
Improved Manufacturing Processes
Advancements in production technology will enhance the precision, quality, and surface treatment of ASTM A53 steel pipes to meet higher application standards.
For instance, the efficiency and quality of seamless pipes (Type S) production will continue to improve, catering to high-performance markets.
Coating and Composite Material Innovations
To address demanding environments such as high corrosion or extreme temperatures, ASTM A53 pipes may increasingly incorporate advanced protective coatings and composite materials.
3. Sustainability Trends
Green Manufacturing and Low Carbon Emissions
Reducing carbon emissions has become a critical focus in the steel industry. ASTM A53 pipe manufacturers are adopting green production techniques, such as energy-efficient steelmaking and recycling scrap steel, to align with the growing demand for environmentally friendly materials.
These improvements not only enhance product competitiveness but also align with global carbon neutrality goals.
Circular Economy Initiatives
The high recyclability of steel pipe materials is a significant advantage for sustainable development. In construction and energy projects, recycling and reusing discarded steel pipes will be an increasingly important practice.
The evolution of the ASTM A53 steel pipe market reflects a dynamic interplay of technological innovation, global economic growth, and sustainability efforts. With its exceptional versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness, ASTM A53 Carbon Steel Pipes continue to meet the needs of diverse industries, from infrastructure development to energy transmission. As the demand for resilient and environmentally sustainable materials grows, ASTM A53 pipes are well-positioned to adapt and thrive. Whether addressing the challenges of high-pressure applications, extreme environments, or green manufacturing, these pipes will remain a cornerstone of industrial progress, driving economic development and supporting global sustainability goals. In navigating future market opportunities, businesses and stakeholders must prioritize understanding these trends to capitalize on the strengths of ASTM A53 steel pipes. This strategic foresight will ensure that they remain competitive and responsive in an ever-changing global landscape!







